With the advances in medical and surgical specialties, blood transfusion has become an essential component of therapy for many serious and common diseases. As a result the demand for blood and blood components has increased throughout the country in the past few years.
Blood transfusion is an essential part of modern day health care. The need for blood is presently increasing due to two reasons:
Like any therapeutic intervention, blood used correctly and judiciously can save life, however it may carry a risk of untoward event e.g. acute or delayed reaction or the risk of transmission of infectious agents such as HIV, Hepatitis viruses, spirochetes and malaria parasites.
We at PRATHAMA BLOOD CENTER always use 100% Blood Components and never whole blood. Whole blood usage is obsolete in modern medicine since 1980’s. Blood is best used, when separated into Red cells, Plasma, Platelets and Cryoprecipitate. All these components have different storage conditions and thus are unstable in whole blood outside human body.
Using blood component therapy saves up to 4 patients from one unit of blood. Prathama remains amongst India’s most modern and the largest blood bank, providing about 1,30,000 units of blood components to needy patients without replacement every year. To support the clinicians in their life saving efforts our Medical team makes more than 3 types of Blood Components & procedures
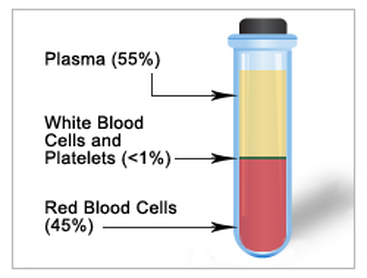
In modern medical treatments, patients may receive specific components of the blood needed to treat their particular condition. This approach to treatment, referred to as blood component therapy, allows several patients to benefit from one pint of donated whole blood. The main transfusable blood components include:
Red cells, or erythrocytes, carry oxygen from the lungs to your body’s tissue and take carbon dioxide back to your lungs to be exhaled.
Platelets, or thrombocytes, are small, colorless cell fragments in the blood whose main function is to interact with clotting proteins to stop or prevent bleeding.
Plasma is a fluid, composed of about 92% water, 7% vital proteins such as albumin, gamma globulin, anti- hemophilic factor, and other clotting factors, and 1% mineral salts, sugars, fats, hormones and vitamins.
Cryoprecipitated Antihemophilic Factor (Cryo) is a portion of plasma rich in clotting factors, including Factor VIII and fibrinogen. It is prepared by freezing and then slowly thawing the frozen plasma.